As PVD coating continues to grow in popularity for knife blades, buyers often have questions about what exactly PVD coating is, its pros and cons compared to other coatings, and how it differs from diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings. This article will provide an in-depth look at PVD knife coating to answer those key questions.

What Is PVD Coating on Knife Blades?
PVD coating utilizes a process called physical vapor deposition to deposit a thin film coating ranging from 2 to 5 microns thick onto knife blades. Inside a vacuum chamber, source materials are evaporated into a vapor that condenses evenly onto the blade surface as it rotates. This allows the vapor to adhere properly across the entire blade.
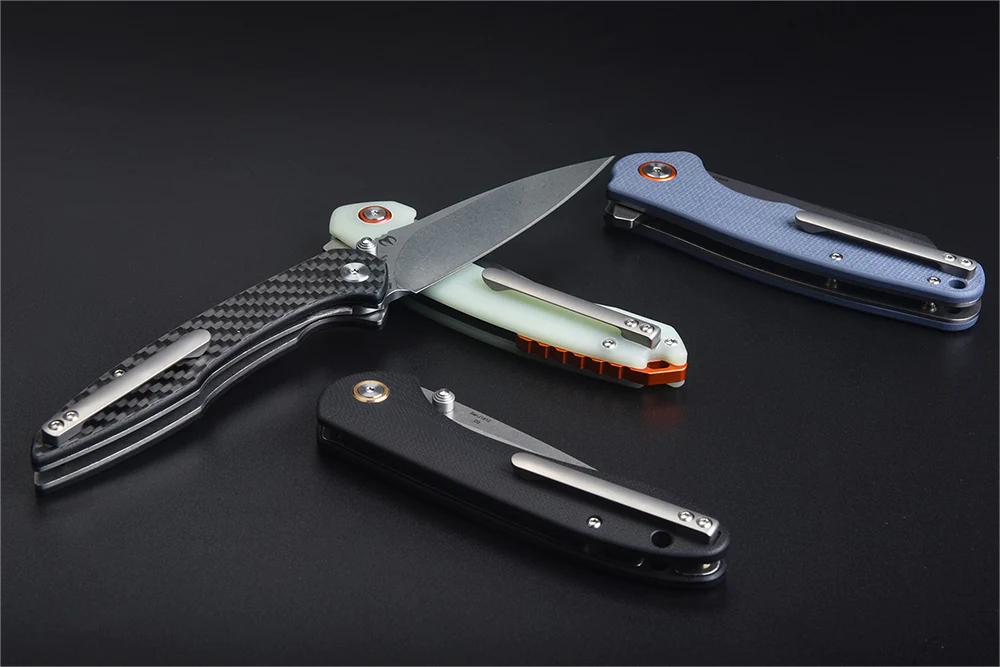
Common PVD coatings for knives include titanium nitride (TiN), titanium carbon nitride (TiCN), titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN), zirconium nitride (ZrN), chromium nitride (CrN), and aluminum titanium nitride (AlTiN). Each material provides slightly different properties.
For example, titanium nitride imparts a gold color while maintaining edge retention and corrosion resistance. Meanwhile, zirconium nitride has a gray appearance while boasting high hardness and durability. The coating material can customize the look and performance.

Advantages of PVD Knife Coatings
Superior Corrosion Protection
The thin PVD films create a protective barrier that significantly improves corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance. By preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the blade surface, rust and staining are effectively halted. Even during continuous use over time, the coating preserves the stainless steel or high carbon steel composition.
Enhanced Scratch Resistance
With hardness ratings in the range of 22-32 on the Rockwell Scale (HRC), PVD coatings make blades more resistant to scratches and edge damage. The hard coating prevents nicks, scuffs, and abrasions across the entire blade face and edge. Durable coatings like titanium aluminum nitride and zirconium nitride even allow the edge to maintain sharpness after heavy use.
Attractive Colored Finishes
Unlike traditional knife finishes restricted to satin, stonewashed, or black appearances, PVD technology creates attractive colored coatings like bright gold, metallic grays, and jet black. Based on the coating composition, customized colors enable consumers to choose blades that match their personal style preferences.
Minimized Thickness for Sharpness
The PVD process deposits very thin coatings, just 2-5 microns thick in most cases. This allows the original cutting edge to remain exposed without significantly impacting sharpness. Chipping and deterioration at the edge only occur after prolonged heavy use.
Secure Bonding
Through precision application in the PVD vacuum chamber, the coating bonds tightly to the blade surface at the atomic level. This creates excellent adhesion that prevents the coating from peeling or flaking off over time. It remains fixed to the blade despite heavy cutting applications.
Eco-Friendly Process
The PVD technique utilizes environmentally friendly processes without relying on hazardous materials. This makes it a clean and non-toxic coating application.

Drawbacks of PVD Knife Coatings
Higher Production Costs
While consumers reap the performance benefits, the added PVD coating process does increase manufacturing costs due to the specialized equipment. These costs translate into higher retail pricing compared to uncoated knife blades.
Potential for Reapplication
Long-term heavy use or abrasion can cause the thin coating to wear away over time, diminishing its protective properties. Refurbishing the coating requires full stripping to remove the old layer before reapplying with pristine PVD films.
Limited Thickness
The 2-5 micron thickness balances durability and sharpness retention but prevents more robust coatings. This can allow small micro-chipping at the very edge after prolonged heavy use.
By weighing the extended corrosion protection, scratch resistance, attractive colors, and sharp bonding against slightly higher costs and eventual reapplication needs, consumers can determine if PVD coatings provide worthwhile advantages for their intended knife use cases. The coating significantly elevates performance while introducing only minor drawbacks.
DLC vs. PVD Knife Coating: What Are the Key Differences?
DLC and PVD knife coatings use advanced deposition techniques to impart thin films onto blades for improved performance. When deciding between the two popular options, here are some key differentiation factors:
1. DLC coatings form through a chemical vapor deposition process, while PVD relies on physical vapor deposition methods. This means DLC enables stronger carbon bonding throughout the coating.
2. DLC can achieve higher hardness ratings in the range of 85+ HRC compared to the 22-32 HRC levels offered by most PVD coatings. This translates to better scratch resistance.
3. PVD produces brighter gold, gray, and colored finishes based on the coating materials used. DLC is restricted to darker black or gray coating aesthetics.
4. Both coating types allow for thin depositions less than 5 microns thick to maintain sharp cutting edges after application. However, DLC coatings can be applied thicker in certain custom cases.
5. While both demonstrate excellent corrosion resistance, DLC generally provides longer working lifespans, between 500-1000% longer than uncoated blades before wear affects performance.
6. The high stability and corrosion resistance of DLC does come at a price premium over PVD coating processes. DLC costs more to produce.
In the end, choosing between PVD and DLC depends on your application needs and budget. DLC will maximize hardness and longevity, while PVD focuses more on decorative custom looks and corrosion resistance – both at excellent value.

Conclusion
PVD coating on knife blades produces durable, attractive, and high-performance edges through the physical vapor deposition process. By considering the coating material and qualities achieved, buyers can select PVD-coated blades that not only showcase unique aesthetics but also deliver marked improvements in corrosion resistance, hardness, and scratch resistance, even with minimal coating thickness.
While PVD boasts many advantages, DLC coating offers even greater hardness and smoothness thanks to its chemical deposition process. This does come at a higher price point. Weight the pros and cons against your usage needs and budget to choose the best-coated blade.
Q&As
Q: What thickness levels are common for PVD coatings on knives?
A: Most PVD coatings are applied at thicknesses between 2-5 microns. This ultra-thin layer maintains the original sharp edge of the blade after deposition while still imparting enhanced properties.
Q: Do PVD coatings add significant weight to a knife?
A: No, the PVD films are extremely thin, adding negligible weight even across an entire knife blade. This allows the knife to maintain the same feel and handling.
Q: Can a PVD-coated blade be resharpened after heavy use?
A: Yes, PVD-coated blades can be resharpened and honed just like uncoated blades. The thin coating does not interfere with the ability to restore an edge after prolonged use causes dullness.
Q: Does DLC coating affect the appearance of Damascus or other blade patterns?
A: No, DLC can be deposited very smoothly and evenly across steel surfaces. It allows the base Damascus or etching patterns underneath to still be visible despite the coating.
Q: What types of steel benefit the most from PVD coatings?
A: High carbon steels and tool steels with lower inherent corrosion resistance gain the most from PVD films. But even stainless steels see improvements in hardness, scratch protection, and colors.
Q: Can a PVD-coated blade be engraved?
A: While difficult, specialized processes like laser engraving can selectively remove the PVD coating to expose the underlying steel for contrasting engraving designs.









Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.